 |
Version 5.2 |
|
|
Real-Time Signals
One of the main functions of the CommuniGate Pro Server is Real-time communication.
Acting as a Signaling Center, the Server receives Real-time signals (Requests) from various sources
(the SIP Module, internal sessions, and "call legs", internal kernel components, etc.).
The Server either processes (terminates) these Requests itself, or it delivers them to
remote entities (via the SIP protocol), or it delivers them to internal sessions and "call legs".
For each Requests, the Signal module optionally generates some provisioning Responses (such as
"Trying" or "Ringing"), and one final Response.
|
|
|
AORs
Users configure their devices (IP phones, AV conferencing tools, Instant Messaging tools)
to connect to a selected Server when they go on-line.
Each user has a unique "XMPP identifier" or "SIP identifier", also called AOR (Address of Record).
For session-less protocols such as SIP, the Server registers the users by remembering their
"SIP identifier" and the network (IP) addresses they use.
Each user may have several registrations active if that user has several
communication devices in the on-line mode (an office IP Phone, a desktop
computer, an instant messaging program on a laptop, etc.)
Registrations allow SIP users to communicate with each other without the
knowledge of the network addresses being used, using just the "SIP identifiers" (AORs).
AORs have the same form as E-mail addresses: username@domainName.
The CommuniGate Pro user AOR is the full name of the user Account, so the user SIP AOR name
is exactly the same as the user E-mail address.
CommuniGate Pro uses the Router component for
all Real-Time Communication operations, so Aliases, Forwarders, and
other Routing methods work for Real-Time Communications, too.
Signals
A Signal is a basic Real-time Task. One Real-time entity sends Signals to some other
Real-time entity to start, modify, or stop a communication dialog, to deliver a status
update, etc.
The sending entity composes a Request object and sends it to the CommuniGate Pro
Signal module. The Signal module processes the Request, optionally sends Requests to other
entities, and returns a Response object to the sending entity.
Many CommuniGate Pro modules and components can use Signals:
- The SIP Module server subcomponent receives Requests from
external Real-time entities (SIP clients, other SIP Servers) using the SIP protocol.
When the Signal Module generates a Response object, the SIP Module sends the response back to the external entity.
- The XMPP Module and XIMSS Module send and receive
Signal Requests and Responses, and transfer them between the client application and the CommuniGate Pro Server.
- Internal Real-time Node, such as Real-Time Application
nodes (such as PBX applications) can send various Signal requests.
- Automated Processing Rules can use Signals (to send Instant Messages as notifications).
Processing Requests
When the Signal Module receives a Request, it calculates the target URI for it.
It takes the Request URI (or the first Route URI in the Request Route set), and uses the
Router component to detect the Request destination. There are
several possible outcomes of this process:
- The Router returned an error code (for example, the Request URI addressed a local Account
that does not exist). This error code is returned to the Signal source, and processing stops.
- The Router returned a non-local address (an address in a non-local Domain). The Request is
passed to the SIP Module for relaying. The Response returned with the SIP
module is passed to the Signal source.
- The Router returned an address of a local internal Real-time Node.
The Request is passed to that Node for processing. The Response returned with the Node is passed to the Signal source.
- The Router returned a local Account address, and the Request can be processed with the Signal
Module itself. The Request is processed, and the Response is returned to the Signal source. This
case includes REGISTER-type Requests and other Requests which URIs target local Domains.
- The Router returned a local address, and the Request cannot be processed with the Signal
Module itself. The the Forking process starts with the Request URI as
the initial AOR set.
The following diagram illustrates the Signal flow inside the CommuniGate Pro Server:
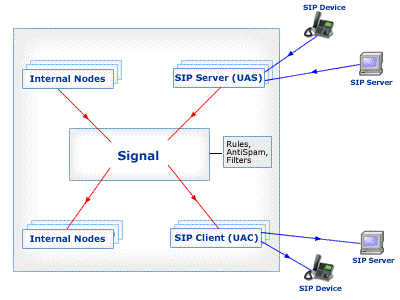
Automated Processing (Rules)
After an address has been processed with the Router, but before it was relayed
to a local or a remote entity, Server-wide and Cluster-wide Automated Signal Processing Rules
are applied.
The Rules control how the Request is processed: they can direct it to a different destination,
or they can reject the Request.
Only the Dialog-initiating Requests are processed with the Automated Rules.
Forking
The Signal module maintains the AOR (Address-of-Record) and Contact sets for each Request it processed.
The module starts the Forking process by processing addresses in the AOR set.
When a 2xx response is received while processing any AOR, AOR processing stops. If the Request
was an INVITE request, all outstanding Requests relayed to other AORs are cancelled.
When all AORs have been processed, the module returns the "best" processing result to the Request source.
When an AOR to be processed is Routed to a non-local address, that address is placed into
the Contact set.
When an AOR to be processed is Routed to a local Group, all Group members
are added to the AOR set.
When an AOR to be processed is Routed to a local Account, all Account
active Registrations (registered addresses of the Account user devices) are added to the Contact set.
If an AOR already exists in the AOR set, it is not added to the AOR set.
If an address already exists in the Contact set, it is not added to the Contact set.
The Signal module checks each address it adds to the Contact set.
If the new Contact address is a Local Node address,
the Request is passed to that Node for processing.
If the new Contact address is an external address, the Request is passed to the SIP Module
for relaying.
When a local or an external entity returns a redirect-type Response, the module checks the initial AOR
(the Request URI).
- If the initial AOR was Routed to a local Account or Group, the addresses specified in the
redirect-type Response are added to the AOR set and the Forking process continues.
- If the initial AOR was Routed to a remote address, the redirect-type Response is returned to
the Request source.
Configuring the Signal Component
You can use the WebAdmin Interface to configure the Signal component.
Open the Real-Time pages in the Settings realm, then open the Signals page:
- Log
- Use this setting to specify the type of information the Signal
component should put in the Server Log. Usually you should use the Failure
(unrecoverable problems only), Major (Signal progress reports),
or Problems (failures, progress reports, and non-fatal errors) levels.
When you experience problems with the Signal component,
you may want to set the Log Level setting to Low-Level or All
Info: in this case the signal processing internals will be recorded
in the System Log. When the problem is solved, set the Log Level setting
to its regular value, otherwise your System Log files will grow in size
very quickly.
The Signal component records in the System Log are marked with the SIGNAL tag.
- Processors
- The Signal component uses several simultaneous processors (threads) to process Signal
"tasks". One processor can handle several Signal tasks.
If you use many time-consuming Automated Rules,
you should allow the component to use more processors for signal processing.
- Object Limit
- This setting specifies how many Signal "tasks" the component can handle at the same time.
If this limit is exceeded, new Signals are rejected, and an error Response is sent to the Signal
sender.
- Event Limit
- This setting specifies the critical number of unprocessed events (sent to all active Signal "tasks").
If this number is exceeded, the component is overloaded (the component Processors cannot handle events as they appear),
new Signals are rejected, and an error Response is sent to the Signal sender.
Sending Signals from Accounts
The CommuniGate Pro Server requires user authentication for certain Requests.
When requests are sent remotely via SIP, authentication is performed with the
SIP module server component.
The XIMSS and XMPP modules send all Signals authenticated, on behalf of the logged-in Account.
The Real-Time Applications send Signals authenticated, on behalf of their current Account (unless the Application has impersonated itself as "nobody").
- Authenticate all outgoing calls
- If this option is selected, the Signal component tries to route the addresses in From fields of the call-type Requests.
If the From address is a local Account address and the request is not authenticated, the Signal component rejects it with the "authentication required" error code.
When a call-type Signal (an initial INVITE request with audio-video Session Descriptor) is authenticated, the Signal Module
peforms additional processing of the authenticated Account.
The Signal component can limit the number of "calls" an Account can place over a specified period of time.
- Reject Outgoing calls
- Use this option to specify a time period and the maximum number of call Signals the Account can place within that time period.
If more calls are placed, they are rejected without processing.
Sending Signals to Accounts
If the first AOR in the set (the AOR specified in the Request URI) is a local Account address,
and the Request is an INVITE request, the Account device registration is retrieved, along with certain Account settings and preferences.
An Account can have Automated Signal Rules, which are retrieved with Account device registrations.
These Rules are "mixed" with the Domain-wide Rules specified for the Account Domain and are applied to all requests sent to the Account.
The Signal component controls how many "calls" (initial INVITE requests with audio-video Session Descriptors) an Account receives over a specified period of time.
- Reject Incoming calls
- Use this option to specify a time period and the maximum number of call Signals the Account can receive within that time period.
If more Signals are received, they are rejected without processing.
Sending Signals to Remote Systems
If a Signal is to be relayed to a remote system, the Signal component directs it to some signaling module.
The Signal target address can be explicitly routed to some module.
For example, all domains with the .xmpp suffix are routed to the XMPP module.
If the Signal target address is not explicitly routed to some module, the Signal component check the target domain name
- If the domain name is an IP address, the Signal is routed to the SIP module.
- If the domain name has SIP SRV records in the DNS, the Signal is routed to the SIP module.
- If the domain name has XMPP SRV records in the DNS, the Signal is routed to the XMPP module.
- In all other cases the Signal is routed to the SIP module.
Service Calls
If a Request is routed to a *nnnn name in any of the local
Domains (where nnnn is any sequence starting with a decimal digit),
the Request is rerouted to its originator (the Request From: address).
This feature allows users to dial a *nnnn number to request a service from
the Server. The Request is routed to the user's own Account, where it starts
the Self-Call application. The application provides the requested service using
the Request To: address to learn the dialed "service option" number.
Registrar Services
Communication devices used by CommuniGate Pro users should register themselves
before they can receive Requests from other entities.
Registration Requests require user authentication.
One Account credentials can be used to modify registrations for
a different Account, if the authenticated Account has the CanImpersonate
access right for the target Account Domain.
To configure the Registrar Service options, open the Real-Time pages in the WebAdmin Settings realm, and select the Signals page.
- Registration: Minimal
- Use this option to specify the minimal Registration expiration time period accepted.
If a Registration Request contains a shorter expiration time, the Request is rejected,
and the Response sent specifies this minimal accepted time. The entity (usually - a SIP device)
can resend the Registration Request with an adjusted expiration time.
- Registration: Default
- This option value is used when a Registration Request does not specify a Registration expiration time.
- Registration: Maximal
- Use this option to specify the maximal Registration expiration time period accepted.
If a Registration Request contains a longer expiration time period, the period is shorten
to the specified value.
- Registration: Random delta
- If this option is set to a non-zero value X, the requested Registration expiration time period is decreased by a random value, from 0 to X.
Large sites can use this feature to soften "registration storms", when a large number of devices starts to register at the same time (after a network failure or a maintenance window).
The requested expiration time period is decreased only if it is larger than 2*X and larger than Minimal+X.
Event Packages
The Signal Module supports several Event Packages. When it receives a SUBSCRIBE Request
targeting a local Account, it may process the Request itself, without forwarding it to the
Account registered entities.
Note: as a workaround for many buggy clients, the Module accepts SUBSCRIBE Requests sent to local Domains (instead of local Accounts).
For these requests, the address in the To field is used to replace the domain-type address in the Request URI.
The Signal module maintains "tuple" states for each Account, for each Event Package it supports.
The module allows one or several entities to update the "tuples", and it aggregates them into one
Account "state information" for the Package. When the aggregated "state information" changes,
the module sends NOTIFY requests with the updated state to all subscribed entities.
The Signal module allows external entities to modify "tuples" using PUBLISH requests.
The Signal module allows external entities to modify "tuples" for certain Packages using
non-standard SERVICE requests.
Presence
The Signal Module implements a Presence Server. The Module supports
the
PIDF,
CPIM-PIDF and
XPIDF Presence Information formats.
The Signal Module provides special processing for the REGISTER requests. If an external
entity (a SIP device) indicates support for the SUBSCRIBE method, the module establishes
a presence subscription dialog with that entity.
The module then processes all NOTIFY requests sent by that entity to maintain
its Presence "tuple" or "segment".
A Presence segment value is a string from a fixed set, listed here starting from the lowest
priority value to the highest priority one:
- offline
- away
- out-lunch
- in-meeting
- be-back
- online
- on-phone
- busy
The event aggregated value is a segment value with the highest priority, or offline if no segment exists.
When a NOTIFY request is composed, the aggregated value is converted into a presence document
in one of the supported formats.
Message Summary
The Signal Module implements the MWI (Message Waiting Indication) Service.
The Module supports the simple-message-summary Information format.
The Server itself maintains the "INBOX" tuple/segment for this Event package.
The segment value is set to an
array:
- the first element is the number of INBOX messages that have the $Media flag set
and do not have the Seen flag set (the number of unread media messages);
- the second element is the number of INBOX messages that have the $Media flag set
(the total number of media messages);
The event aggregated value is an array containing the by-element sum of all segment array values.
When a NOTIFY request using the simple-message-summary Information format
is composed, the first aggregated array element value is used as the number of new voice messages,
and the difference between the second and the first elements is used as the number of old voice messages.
If the first array element value is not zero, the Messages-Waiting element is set to
yes, otherwise it is reset to no.
Subscription to the Message Summary package is available to the Account owner,
and to other Accounts with the CanImpersonate Access Right.
Registration
The Signal Module implements the Registrar Monitoring Service.
The Module supports the reginfo+xml Information format, and it can
inform network entities (such as SIP clients) about all other entities registered
with an Account.
Subscription to the Registration package is available to the Account owner,
and to other Accounts with the CanImpersonate Access Right.
Dialog
The Signal Module implements the Dialog Monitoring Service.
The Module supports the dialog-info+xml Information format, and it can
inform network entities (such as SIP clients) about all dialogs active with an Account.
Subscription to the Dialog package is available to the Account owner,
and to other Accounts with the CallControl Access Right granted by with Account owner.
Dialogs
The CommuniGate Pro Server can create Dialog objects when processing certain INVITE requests.
Dialog objects contain information about the call/session/dialog created with these requests.
Dialog objects are destroyed when the call/session/dialog created with the INVITE request is terminated.
An INVITE request creates a Dialog object if any of the following conditions is met:
- the request sender is authenticated;
- the request target is a local Account;
- a Media Proxy is needed to handle the call;
If the caller is authenticated, the call status is recored in the caller Account data, and a CDR record is generated.
When a call is completed, an accounting record for this outgoing call is added to the caller Account log files.
If the call target (callee) is authenticated, the call status is recored in the callee Account data, and a CDR record is generated.
When a call is completed, an accounting record for this incoming call is added to the callee Account log files.
When the authenticated peer (the caller or the callee) places a call on hold, their Account "Hold Music" preference is used.
If it is not set to disabled, the specified sound file is read from the Account File Storage.
If the file name is "*" or if the specified file is not found, the HoldMusic file is read from the Account Domain Real-Time Application Environment.
When the sound file is read, a Media Channel is created and instructed to play the retrieved file to the other peer.
You can use the WebAdmin Interface to configure the Dialog Manager component.
Open the Real-Time pages in the Settings realm, then open the Signals page:
- Log
- Use this setting to specify the type of information the Dialog Manager
component should put in the Server Log. Usually you should use the Failure
(unrecoverable failures only), Major (failures and major events),
or Problems (failures, major events, and non-fatal errors) levels.
The Dialog Manager component records in the System Log are marked with
the DIALOG tag.
- Time Limit
- This setting specifies a time limit for Call Dialogs. When this limit is exceeded, the Dialog object
(and its Media Proxy, if any) is removed. Keep this limit high enough to avoid call interruptions.
- Signal Idle Timeout, Media Idle Timeout
- If there is no signal sent within a Dialog for the specified period of time, and, if a Media Proxy
is associated with that Dialog, there no media data to relay for the specified period of time, that Dialog object is removed.
Keep these limits high enough to avoid call interruptions when a call is placed on hold.
Local Nodes
The CommuniGate Pro Server dynamically creates, runs, and removes Real-Time Nodes.
A Node is an internal CommuniGate Pro Server object that can receive Signal Requests
and produce Responses for those Requests. A Node can also send Requests and process Responses.
Various CommuniGate Pro components and modules use Nodes to implement Signaling functions:
- The Real-Time Application component creates a Node for each "call leg".
- The MAPI and WebUser modules create Real-Time
Nodes to implement the "Make Call" function. The Node these modules create sends Requests to
establish a call between the session user and the specified address.
- The SIP Module creates a Node and uses it to send Register Requests to External
Gateways to maintain the Server Registration on those Gateways.
- The Presence subcomponent creates a Node and uses it to manage Presence Event
Subscriptions for those devices that cannot proactively update their Presence state.
You can use the WebAdmin Interface to configure the Nodes component.
Open the Real-Time pages in the Settings realm, then open the Nodes page:
- Log
- Use this setting to specify the type of information the Local Nodes
component should put in the Server Log. Usually you should use the Failure
(unrecoverable failures only), Major (failures and major events),
or Problems (failures, major events, and non-fatal errors) levels.
When you experience problems with the Local Nodes component,
you may want to set the Log Level setting to Low-Level or All
Info: in this case the Node processing internals will be recorded
in the System Log. When the problem is solved, set the Log Level setting
to its regular value, otherwise your System Log files will grow in size
very quickly.
The Local Nodes component records in the System Log are marked with
the NODE tag.
- Processors
- The Local Nodes component uses several simultaneous processors (threads) to process
Nodes. One processor can handle several Nodes tasks.
If you use many Nodes implementing time-consuming operations (complex Real-Time Applications, etc.)
you should allow the component to use more processors.
- Object Limit
- This setting specifies how many Nodes the component can handle at the same time.
If this limit is exceeded, attempts to create new Nodes result in an error.
- Event Limit
- This setting specifies the critical number of unprocessed events (sent to all active Nodes).
If this number is exceeded, the component is overloaded (the component Processors cannot handle events as they appear),
and attempts to create new Nodes result in an error.
Call Legs
The Server creates special Local Nodes called Call Legs. Each Call Leg terminates signaling
for one phone call. Each PBX Task is a Call Leg, and each XIMSS session
can create one or more Call Legs to handle phone calls initiated or accepted by the XIMSS session user.
The settings in the Call Legs panel are applied to all types of Call Legs:
- Session-Expiration
- Use this setting to specify how often the parties should exchange the INVITE (or OPTION) requests to verify that the call has not been broken.
- Hop Limit
- Use this setting to specify the Max-Forwards field value for the requests sent with Call Legs.
- Adverise UPDATE
- If this option is enabled, the requests sent with Call Legs include the UPDATE method in their Allow fields.
- Send UPDATE
- If this option is enabled and the other party advertises support for the UPDATE method, Call Legs use the
UPDATE method (instead of the INVITE method) for session refresh requests.
Call Detail Records (CDRs)
The Signal module can generate Call Detail Records for INVITE and BYE transactions it processes.
It can also generate Call Detail Records for completed calls using the information in the Dialog objects.
CDRs can be generated and stored in CDR Log files.
CDR Log files are stored in the
base directory, inside the CDRs subdirectory of the SystemLogs subdirectory.
CDR Log files are text files, with each record stored as a separate line.
Each CDR line has the following format:
- hh:mm:ss.ddd cdr_data
where
hh is the hour,
mm is the minute,
ss is the second, and
ddd is the
millisecond of the moment when the CDR record was generated, and the
cdr_data is the CDR data.
- Record Call CDRs
- Select this option to generate CDR Log files for Calls (Dialog objects).
- Record INVITE/BYE CDRs
- Select this option to generate CDR Log files for INVITE and BYE requests.
When the External CDR Processor Helper application is enabled,
the Signal Module generates all types of CDRs and sends them to that application.
CDR data text for INVITE/BYE requests has the following format:
- 01 NNN-method <callID><fromTag><toTag> <from><to> [reqIP][respIP] flags
where:
- 01
- the CDR format version number
- NNN
- the transaction result code (numeric)
- Method
- the transaction operation/method (INVITE, BYE).
- callID, fromTag, toTag
- the dialog Identifier (the Call-ID field, the From field tag parameter, the To field tag parameter).
Note: If a call is terminated by the callee, the fromTag of the BYE transaction is the toTag of the INVITE transaction and vice versa.
- from, to
- the transaction From and To field URIs.
- reqIP
- the network (IP) address the transaction request was received from.
- respIP
- the network (IP) address the transaction response was received from.
- flags
- optional elements, separated with space symbols:
- [auth:accountName]
- this element is added if the transaction request is authenticated. The accountName is
the name of the authenticated CommuniGate Pro Account.
- [redir:accountName]
- this element is added if the transaction request was redirected from a local Account. The accountName is
the name of that CommuniGate Pro Account.
- [billing:billingData]
- this element is added if the transaction request has a P-Billing-Id field. The billingData string is
the field content.
- [referred:referredby]
- this element is added if the transaction request has a Referred-By field. The referredby string is
the field content.
CDR data text for calls has the following format:
- 02 callType accountName alertTime connectTime reason <callID><fromTag><toTag> ["fromName"] <from> ["toName"]<to>[[toProgramName]] flags
where:
- 02
- the CDR format version number
- callType
- the call type (INP, OUT).
- accountName
- the full Account name (accountName@domainName).
- alertTime
- the time period (in seconds) between the time the call was initiated and the time the call was accepted or rejected.
- connectTime
- the time period (in seconds) between the time the call was accepted and the time the call was terminated. If the call was not accepted, this field contains the - (minus) symbol.
- reason
- the reason the call was rejected or terminated.
- callID, fromTag, toTag
- the dialog Identifier (the Call-ID field, the From field tag parameter, the To field tag parameter).
- from, to
- the transaction From and To field URIs.
- fromName, toName
- the transaction From and To field "real names".
- toProgramName
- optional - the name of the PBX Application that has accepted the call.
- flags
- the same as used with version 01 records.
Signal API
The Signal tasks can receive "events" from other CommuniGate Pro components, such as CG/PL tasks
and XIMSS client sessions. To send an event, the sender should obtain a signal handle.
A Signal task accepts the following events:
- decline
- This event causes the Signal task to cancel Signal Request processing and to reject it with the 603 Decliened error code.
- fork
- This event data should be a string or an array of strings. The Signal Request is forked to the URIs specified with these strings.
- redirect
- Same as fork, but all currently "forked" Requests are cancelled.
CommuniGate® Pro Guide. Copyright © 1998-2009, Stalker Software, Inc.


